The Significance of Melanin: Understanding Its Role in Skin and Health
Melanin is a crucial natural pigment found in the skin, hair, and eyes of humans and animals, contributing to the color of these features. The primary function of melanin is to provide protection against harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Without this important pigment, our bodies would be far more vulnerable to the deleterious effects of UV exposure, which can lead to skin issues and even skin cancers.
What is Melanin?
Melanin is produced in the skin by specialized cells called melanocytes. These cells are situated in the basal layer of the epidermis, the skin's outermost layer. Melanin comes in several forms, primarily eumelanin, pheomelanin, and neuromelanin, each contributing different shades ranging from black and brown to red and yellow. The predominance of one type of melanin over another gives individual skin and hair its unique color.
The Functionality of Melanin in Skin Health
- Sun Protection: Melanin absorbs harmful UV rays, reducing the risk of skin damage.
- Skin Tone Variation: Different concentrations of melanin result in various skin tones, from fair to dark.
- Antioxidant Properties: Melanin can help neutralize free radicals, potentially reducing the risk of some skin conditions.
- Thermal Regulation: Melanin has a role in modulating skin temperature during exposure to heat.
Melanin and Skin Cancer: What You Need to Know
Understanding the relationship between melanin levels and the risk of skin cancer is essential. Generally, individuals with higher levels of melanin have greater protection against skin cancer. However, this does not mean that individuals with darker skin are invulnerable. Skin cancer can still affect them, thus making it imperative for all individuals, regardless of skin tone, to engage in proper skin care and monitoring.
The Importance of UV Protection for All Skin Types
Everyone, no matter how much melanin they have, should adopt a comprehensive UV protection strategy. This includes:
- Using broad-spectrum sunscreens with a minimum SPF of 30.
- Wearing protective clothing and hats during intense sunlight.
- Seeking shade whenever possible, especially during peak hours.
Melanin and Its Impact on Beauty and Skin Care
The beauty industry has evolved significantly with growing awareness about melanin. Products that enhance or complement serotonin levels have gained popularity. The phrase “melanin 2” highlights an emerging focus on skincare that not only considers different skin tones but also addresses the specific needs of those tones.
Skincare Products and Melanin
Brands enhancing their formulations to target different levels of melanin acknowledge that skincare is not one-size-fits-all. Products developed for various skin types not only cleanse and hydrate but also aim to balance pigmentation. Here are some types of products popular among consumers:
- Brightening Creams: These creams help reduce hyperpigmentation and promote an even skin tone.
- Moisturizers with Vitamin C: Vitamins can help improve melanin production, thus contributing to a healthier glow.
- SPF Products: Sunscreens formulated for darker skin tones to avoid white cast while still providing effective UV protection.
- Serums: Concentrated products that target smoothing and brightening features through enhanced absorption of nutrients.
Understanding the Science Behind Melanin Production
The production of melanin is stimulated by exposure to sunlight, a process known as melanogenesis. This process helps the skin produce more pigment as a defense mechanism against UV rays. The enzyme tyrosinase plays a vital role in this process by catalyzing the conversion of tyrosine into melanin.
Factors Influencing Melanin Production
Several factors impact the quantity and quality of melanin produced in individuals:
- Genetics: Family history can determine skin color and susceptibility to pigmentation disorders.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause can affect melanin levels.
- Age: As we age, melanin production often decreases, leading to grey hair and lighter skin tones.
- Sun Exposure: The amount and frequency of sun exposure will influence the degree of melanin production.
Melanin and Health: Beyond the Skin's Surface
It is vital to recognize that melanin does not just exist to give color to our skin and hair—it plays a role in our overall health.
Impact of Melanin on Physical Health
Recent studies have even explored the links between melanin and several illnesses:
- Parkinson's Disease: Neuromelanin, a type of melanin found in the brain, has been researched for its potential relationship with Parkinson's disease.
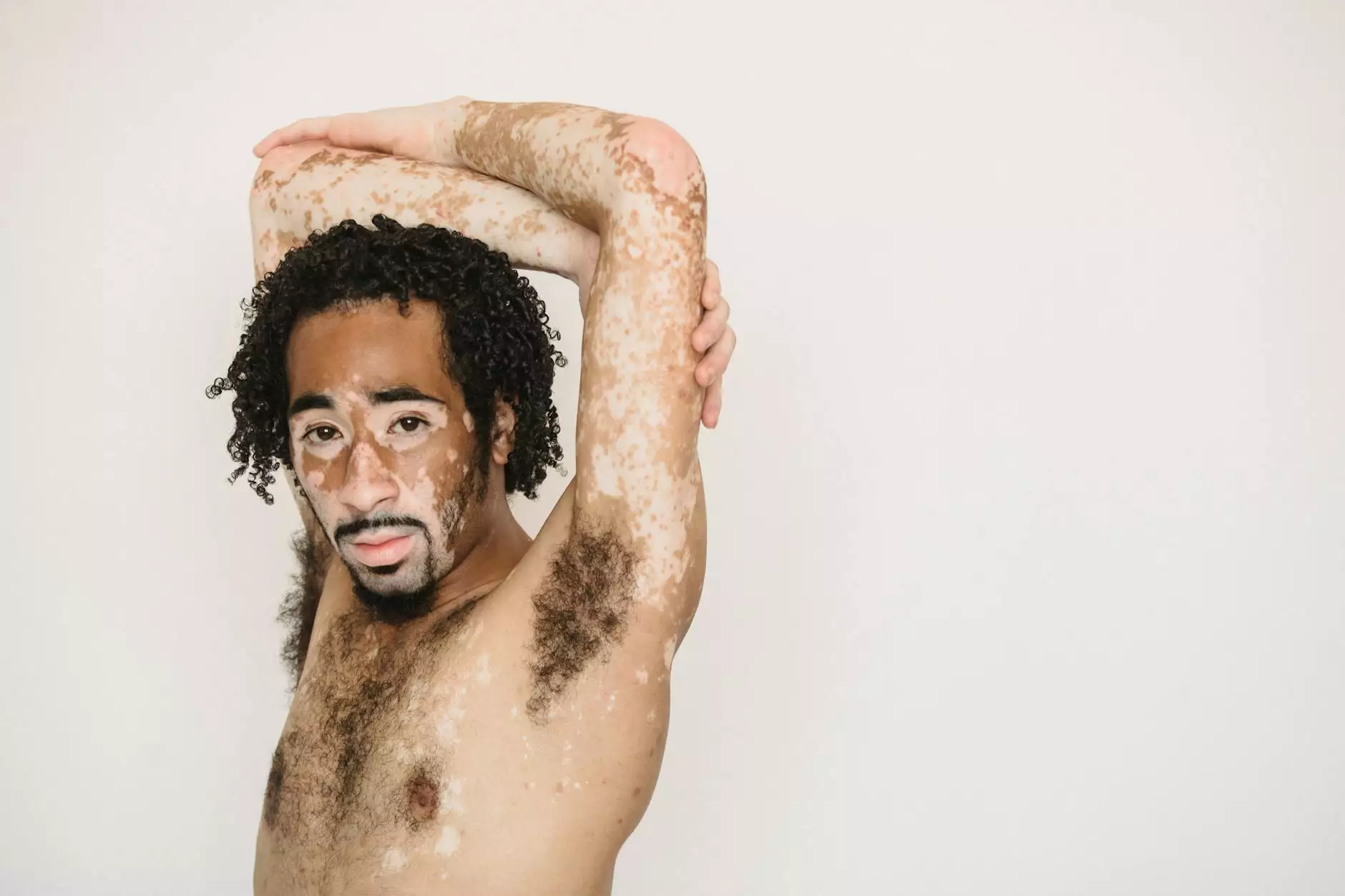
- Skin Disorders: Conditions such as vitiligo and melasma are also linked to the body's ability to produce melanin efficiently.
- Immune Function: Some studies suggest that melanin may play a role in immune responses and overall body defense mechanisms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, melanin is more than just a pigment; it is a pivotal element of human biology that affects our skin, health, and even beauty standards. As we advance our understanding of melanin, we can foster better skincare solutions that cater to the unique needs of individuals across all skin tones. The integration of science with skincare offers a new frontier for developing effective products targeted at varying melanin levels, which ultimately enhances the beauty and health of our skin. Recognizing, celebrating, and respecting the roles of melanin can pave the way for more inclusive beauty standards and a healthier society.